Custom as A Source of Law

Meaning & Definitions of Jurisprudence
Introduction
The word ‘custom’ is derived from an old French word ‘Costume’. Some says that the word ‘custom’ is based on Latin word ‘Consuetudo’. In Hindi the word ‘custom’ means ‘reeti’,‘vyavahar’,‘rasm’, or ‘riwaj’.Custom enjoys a very important place in every legal system.
Uniformity of human conduct in similar circumstances is called custom.
Definitions
According to Salmond: –
“Custom is the embodiment of those principles which have commended themselves to the national conscience as principles of justice and public utility.”
We can say that the principles that are acknowledged and approved not by the power of the state, but by public opinion of the society at large.
Holland: –
He defined custom as “a generally observed course of conduct.” The best illustration of the formation of such habitual courses of action is the mode in which a path is formed across a common law.
Allen :-
According to Allen, “custom arises partly from necessity and partly from the forces of intuition and imitation.”
Kartor :-
According to Cartor, “the uniformity of the actions of all the people in the same circumstances is called custom.”
Austin: –
According to Austin, “custom is a rule of conduct which the governed observe spontaneously and not in pursuance of law set by a political superior”.
Halsbury: –
Custom is some kind of special rule which is in actual existence and possible followed from time immemorial and which has acquired the force of law in a specified territory, although it may be contrary to or inconsistent with the general law of the land.
Harprasad v. Shivdayal:- In this case the judicial committee of the Privy Council observed, custom as a rule which in a particular family or in a particular district or in a particular section, class or tribe, has from long us age obtained the force of a law.
Origin of custom: –
Jurists have contradiction in the relation of origin of customs. According to Savigny Custom originated from the people’s subconscious pattern. Allen and Paton criticized it.
- According to some jurists, customs originate because of necessity or convenience.
- According to historical school customs have their basis in the common consciousness of the people,
- According to Analytical school judicial decisions are the basis of customs.
- Custom came into existence because of the tendency of human beings to imitate each other.
According to Henery men, custom is such a perception which came into existence after the goddess of justice (thimistese)
In terms of convenience, the origin and development of custom can be studied in 3 stages.
- In the first stage, custom is uncertain.
- Being in vogue for some time brings certainty in it. After this it has to be proved before the court. Then it becomes customary law, that is, it takes the form of a law.
- Custom is finally enacted by legislation.
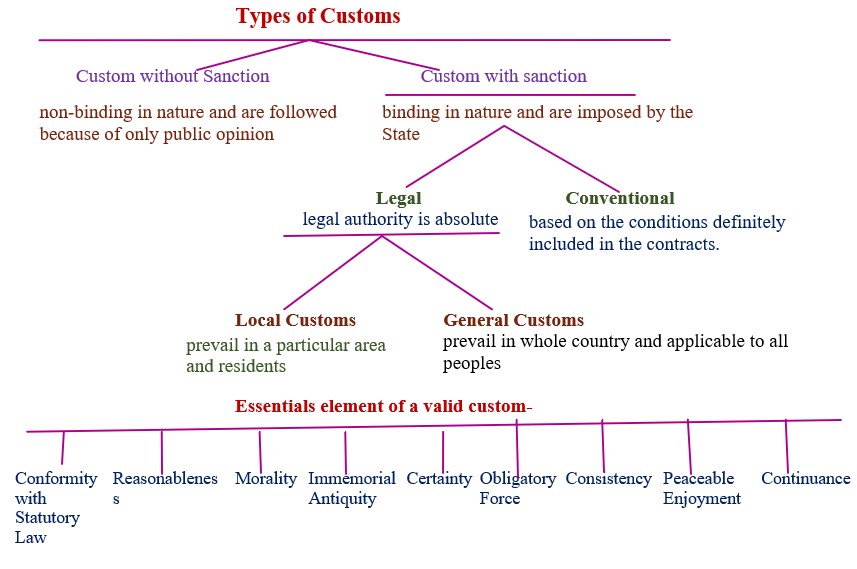
Types of Customs
- Custom without Sanction
- Customs with Sanction
Custom without Sanction:-
The customs are non-binding in nature and are followed because of only public opinion.
Custom with sanction :-
The customs are binding in nature and are imposed by the State.
Classification of customs according to salmond:-
Salmond has devided customs with sanction in two types:- Legal & Conventional customs
- Legal :- Legal customs are automatically created as binding rules of law. Their legal authority is absolute. These customs are further divided in two categories.
- Conventional :- Conventional customs are based on the conditions definitely included in the contracts.
Legal Customs are further divided in two types:-
- Local Customs :-Local customs are prevail in a particular area and residents of that particular area follow only.
- General Customs:-General Customs are prevail in whole country and applicable to all peoples of the nation generally.
Essentials element of a valid custom-
- Conformity with Statutory Law
- Reasonableness
- Morality
- Immemorial Antiquity
- Certainty
- Obligatory Force
- Consistency
- Peaceable Enjoyment
- Continuance
There is a difference of opinion among jurists regarding when a custom law is made.
According to Austin and Allen, supporters of analytical ideology, custom becomes law only after a custom is recognized by the sovereign.
According to the historical jurist, custom is law in itself, it is based on public opinion and national character. custom is law independently of any declaration or recognition by the state
FAQs
- Give some examples of customary law?
Answer : Here are some examples of customary Law:-
- Indigenous customary law among native communities.
- Business customs and practices in commercial law.
- Family and marriage customs in family law.
- Religious customs and rituals that have legal significance.
2. What are essentials to prove customs in legal context?
Answer : There should be Conformity with Statutory Law, Reasonableness, Morality, Immemorial Antiquity, Certainty, Obligatory Force, Consistency, Peaceable Enjoyment to prove customs in legal context.
3. Can custom overrule written laws?
- Yes, In some cases custom can overrule written laws if the custom is well-established and widely accepted within a legal system.
